Visual Studio (VS) 配置
包含目录、库目录、附加包含目录、附加库目录、附加依赖项之详解_附加包含目录和附加库目录的区别
三类文件 .h,.lib,.dll
首先添加工程头文件 .h:
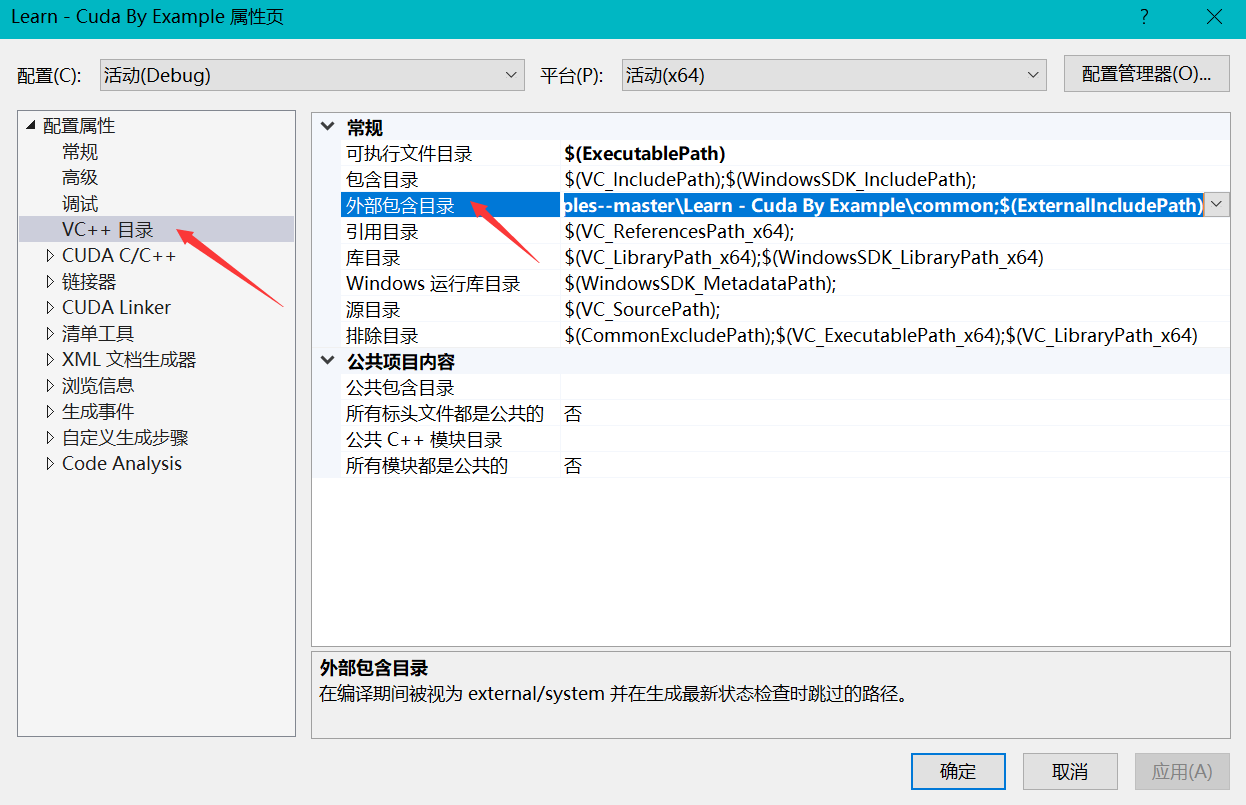
然后添加工程引用的 .lib 库路径:
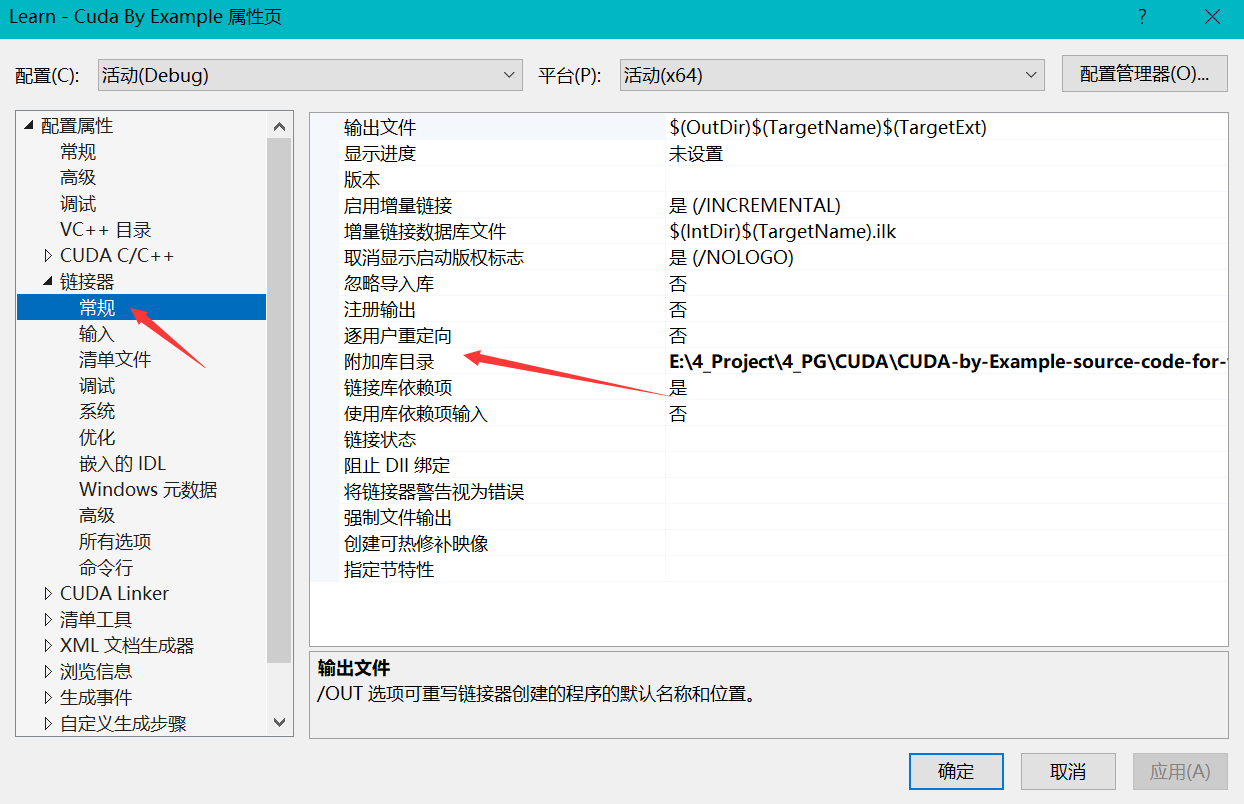 同时添加工程引用的
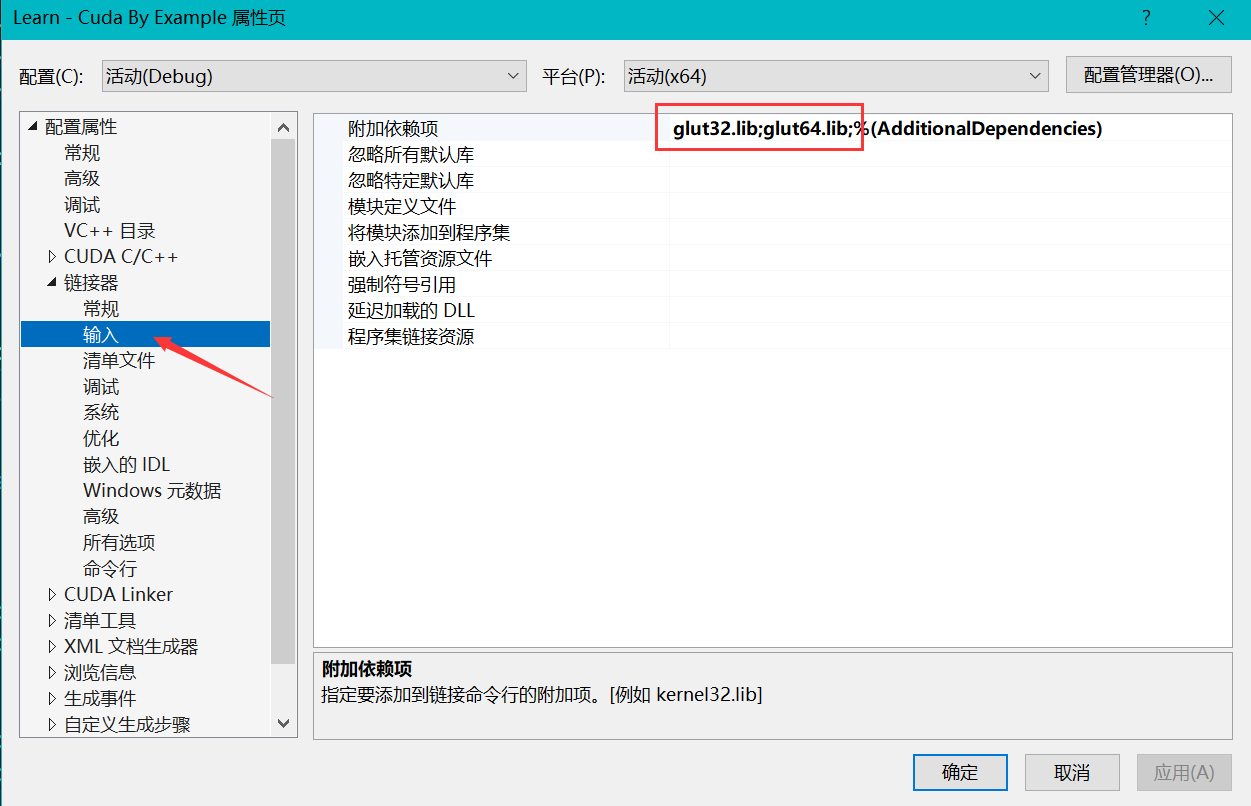
同时添加工程引用的 .lib 文件名
最后将动态链接库 .dll 放在可执行文件 .exe 目录下,例如
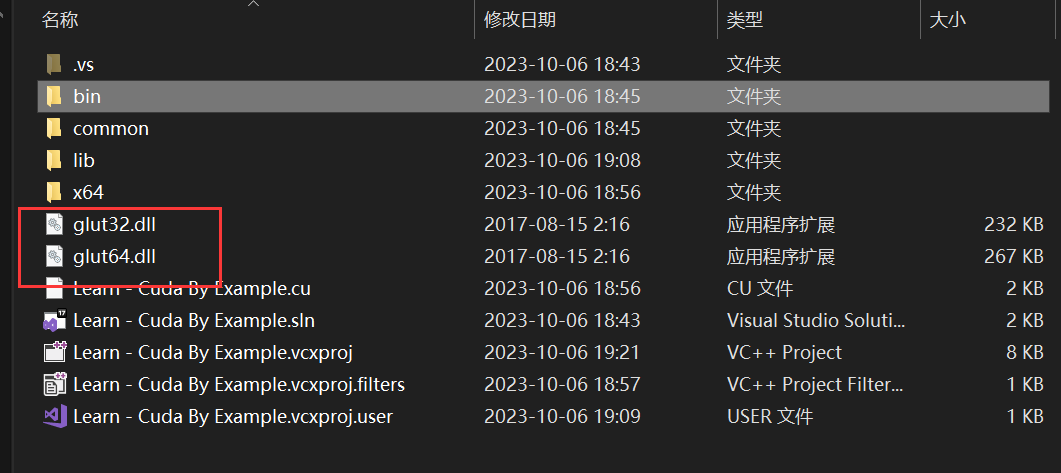 一般来说,bin 文件夹都会加到系统环境变量中,但这里我们省略,直接放在文件目录下
一般来说,bin 文件夹都会加到系统环境变量中,但这里我们省略,直接放在文件目录下
lib 库默认路径:C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v12.0\lib
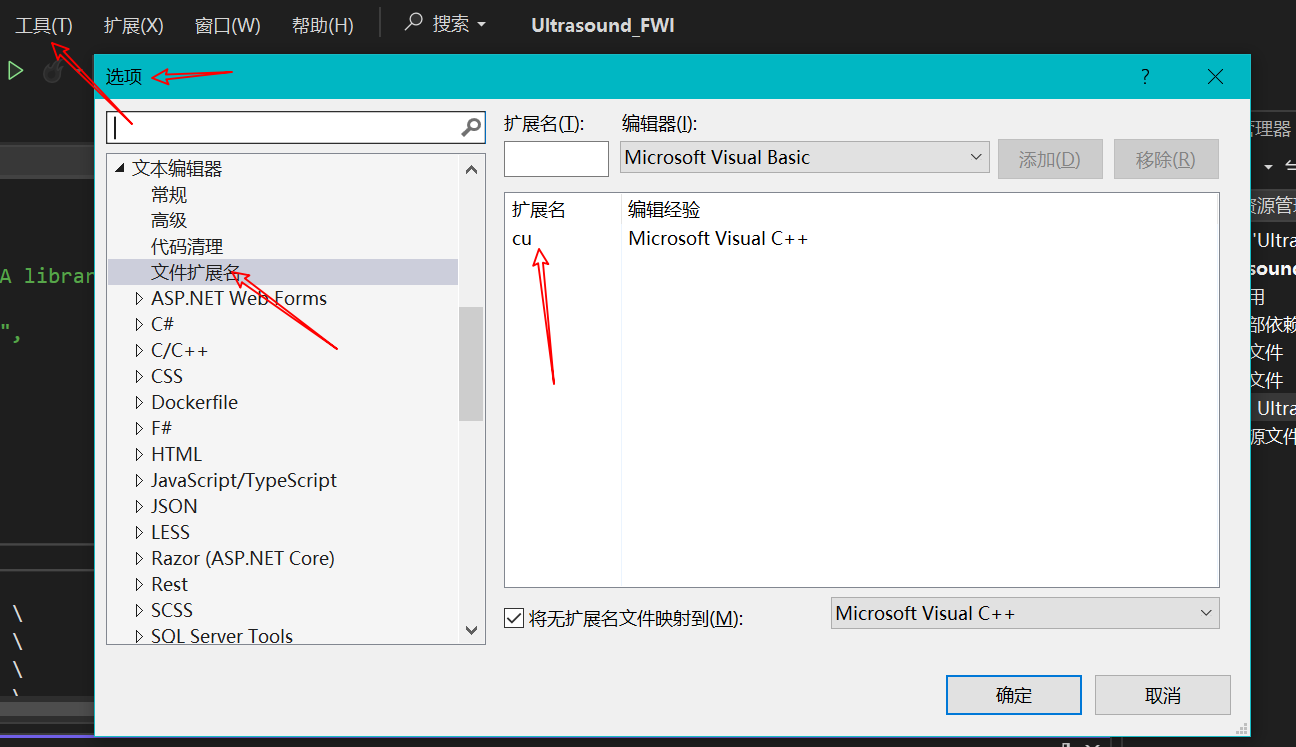
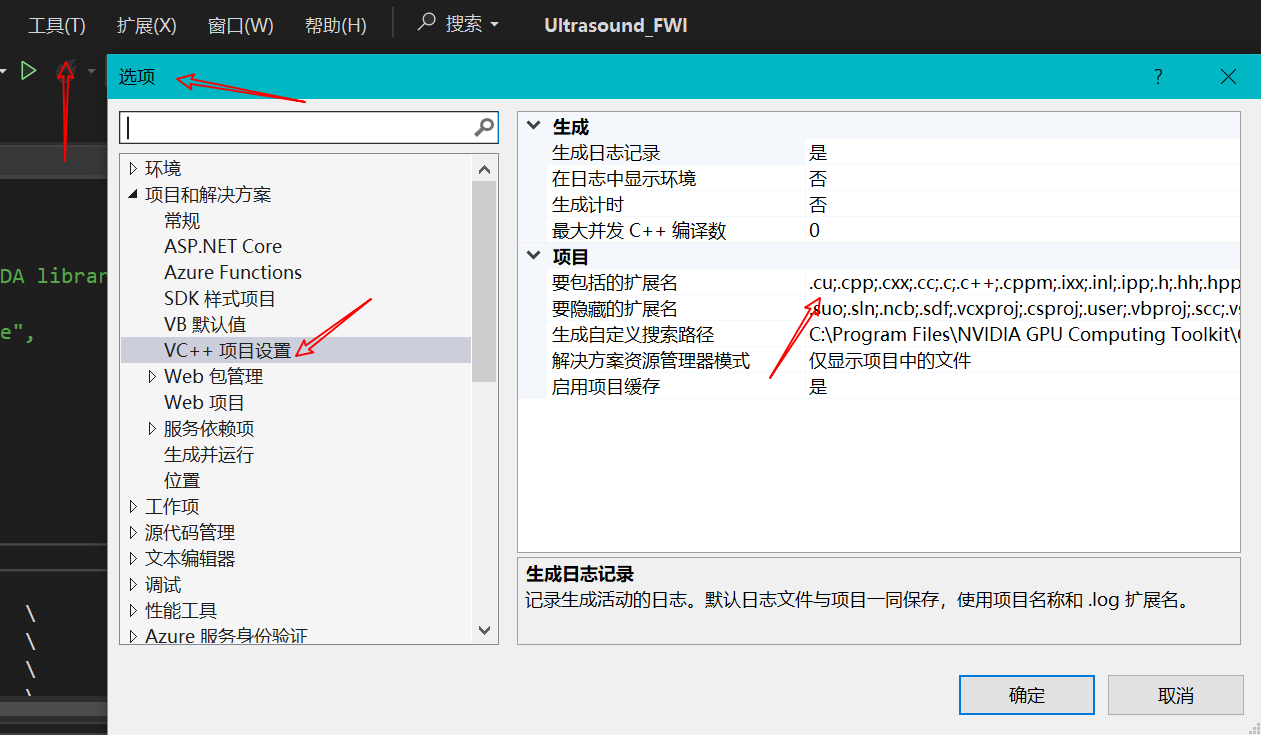
CUDA 配置
CUDA Build Customization
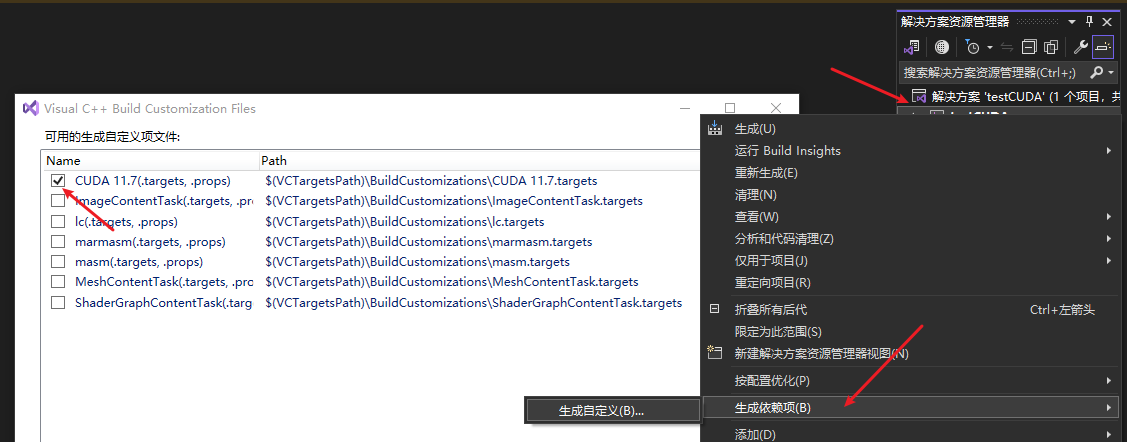
测试样例
测试样例 1:打印显卡配置
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int deviceCount;
cudaGetDeviceCount(&deviceCount);
int dev;
for (dev = 0; dev < deviceCount; dev++)
{
int driver_version(0), runtime_version(0);
cudaDeviceProp deviceProp;
cudaGetDeviceProperties(&deviceProp, dev);
if (dev == 0)
if (deviceProp.minor = 9999 && deviceProp.major == 9999)
printf("\n");
printf("\nDevice%d:\"%s\"\n", dev, deviceProp.name);
cudaDriverGetVersion(&driver_version);
printf("CUDA驱动版本: %d.%d\n", driver_version / 1000, (driver_version % 1000) / 10);
cudaRuntimeGetVersion(&runtime_version);
printf("CUDA运行时版本: %d.%d\n", runtime_version / 1000, (runtime_version % 1000) / 10);
printf("设备计算能力: %d.%d\n", deviceProp.major, deviceProp.minor);
printf("Total amount of Global Memory: %u bytes\n", deviceProp.totalGlobalMem);
printf("Number of SMs: %d\n", deviceProp.multiProcessorCount);
printf("Total amount of Constant Memory: %u bytes\n", deviceProp.totalConstMem);
printf("Total amount of Shared Memory per block: %u bytes\n", deviceProp.sharedMemPerBlock);
printf("Total number of registers available per block: %d\n", deviceProp.regsPerBlock);
printf("Warp size: %d\n", deviceProp.warpSize);
printf("Maximum number of threads per SM: %d\n", deviceProp.maxThreadsPerMultiProcessor);
printf("Maximum number of threads per block: %d\n", deviceProp.maxThreadsPerBlock);
printf("Maximum size of each dimension of a block: %d x %d x %d\n", deviceProp.maxThreadsDim[0],
deviceProp.maxThreadsDim[1],
deviceProp.maxThreadsDim[2]);
printf("Maximum size of each dimension of a grid: %d x %d x %d\n", deviceProp.maxGridSize[0], deviceProp.maxGridSize[1], deviceProp.maxGridSize[2]);
printf("Maximum memory pitch: %u bytes\n", deviceProp.memPitch);
printf("Texture alignmemt: %u bytes\n", deviceProp.texturePitchAlignment);
printf("Clock rate: %.2f GHz\n", deviceProp.clockRate * 1e-6f);
printf("Memory Clock rate: %.0f MHz\n", deviceProp.memoryClockRate * 1e-3f);
printf("Memory Bus Width: %d-bit\n", deviceProp.memoryBusWidth);
}
return 0;
}
测试样例 2:向量相加
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size);
__global__ void addKernel(int *c, const int *a, const int *b)
{
int i = threadIdx.x;
c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
int main()
{
const int arraySize = 5;
const int a[arraySize] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
const int b[arraySize] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
int c[arraySize] = { 0 };
// Add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t cudaStatus = addWithCuda(c, a, b, arraySize);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addWithCuda failed!");
return 1;
}
printf("{1,2,3,4,5} + {10,20,30,40,50} = {%d,%d,%d,%d,%d}\n",
c[0], c[1], c[2], c[3], c[4]);
// cudaDeviceReset must be called before exiting in order for profiling and
// tracing tools such as Nsight and Visual Profiler to show complete traces.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceReset();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceReset failed!");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Helper function for using CUDA to add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size)
{
int *dev_a = 0;
int *dev_b = 0;
int *dev_c = 0;
cudaError_t cudaStatus;
// Choose which GPU to run on, change this on a multi-GPU system.
cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice(0);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?");
goto Error;
}
// Allocate GPU buffers for three vectors (two input, one output) .
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_a, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_b, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
// Copy input vectors from host memory to GPU buffers.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
// Launch a kernel on the GPU with one thread for each element.
addKernel << <1, size >> > (dev_c, dev_a, dev_b);
// Check for any errors launching the kernel
cudaStatus = cudaGetLastError();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addKernel launch failed: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus));
goto Error;
}
// cudaDeviceSynchronize waits for the kernel to finish, and returns
// any errors encountered during the launch.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceSynchronize();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel!\n", cudaStatus);
goto Error;
}
// Copy output vector from GPU buffer to host memory.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
Error:
cudaFree(dev_c);
cudaFree(dev_a);
cudaFree(dev_b);
return cudaStatus;
}
.cu 文件中在声明使用 CUDA 线程数可能在:<<< >>> 符号处报错,不用管,能够运行就行,该符号在 cpp 文件中是不能编译的,但是 cu 文件的编译方法与 cpp 不一样。
cpp 文件中不要 #include <xxx.cu> 文件,直接声明函数并使用。如果 include,相当于把 .cu 文件中的代码用 cpp 编译,<<<>>> 则会报错。
例如
/*main.cpp文件*/
void add(int num);
int main(void)
{
/*调用CUDA*/
add(5000);
return 0;
}
/*add.cu文件*/
/*核函数(设备运行函数)*/
__global__ void vectorAdd(const float* A, const float* B, float* C, int numElements)
{
int i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < numElements)
{
C[i] = A[i] + B[i] + 10;
}
}
/*主机函数*/
void add(int num)
{
/*生成主机数组内存 h_A, h_B, h_C*/
int numElements = num;
size_t size = numElements * sizeof(float);
float* h_A = (float*)malloc(size);
float* h_B = (float*)malloc(size);
float* h_C = (float*)malloc(size);
/*...*/